Safety Diode Transistor Opamp Triac
Thyristor
Target Preparing Experimentation Report Problems
Laboratory target
Making the simple thyristor circuits and acquainting with input and output characteristics of a thyristor.
Lesson preparation
- Using the datasheet below, find the thyristor data: type, maximum forward current IF max, forward voltage UF max, reverse voltage UR max, gate voltage UG max, and gate current IG max.
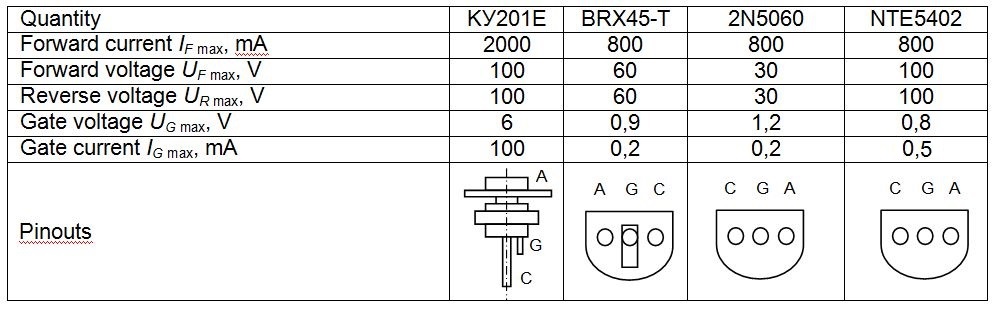
- Familiarise with the available power source: its voltage Us max, and current Is max.
- Develop the circuit and wiring diagrams to study an input characteristic IG(UGC) at an open anode-cathode circuit and output characteristic IF(UF) of a thyristor. Calculate and set a voltage divider between the power source and the gate circuit to protect the power source and gate from overloading. Calculate and set another voltage divider between the power source and the anode/cathode circuit to protect the thyristor. Choose the potentiometers of 1 kΩ or 10 kΩ in these dividers.
- Provide the circuit link-up with:
dc voltmeter PV to measure the gate voltage UGC or the thyristor voltage UF
dc ammeter PA to measure the gate current IG or the thyristor current IF
and propose the required meters: their types, measuring limits, and maximum measured values.
- Sketch expected input and output characteristics and voltage waveforms.
Experimentation
- Choose the meters and set the required measuring ranges and sockets for wiring. Adjust the supply voltage to 10 V.
- Find the positions of the potentiometers that correspond to the maximal and minimal voltages and set the minimal voltages on their outputs.
- Assemble the desired circuit to estimate the input characteristic IG(UGC) at an open anode-cathode circuit. Self-examine the assembled circuit and ask the instructor to examine it.
- Power on the supply source and ensure the circuit operates properly. If the fault occurs in any instant, power off the lab bench immediately, examine the circuit and eliminate errors.
- To estimate an input characteristic, increase smoothly the gate voltage by the gate potentiometer until the accessible gate current or maximal gate voltage is achieved. At every step, measure the gate voltage and current, fill the measured values in the protocol, and plot the graph. Afterwards remove the gate voltage and the breadboard supply.
- Assemble the desired circuit to estimate the output characteristic IF(UF), self-examine and ask an instructor to check it. Make sure the gate voltage is zero.
- To plot an output characteristic, set the maximal accessible thyristor voltage UF and increase smoothly the gate voltage until the thyristor opens (i.e. until UF drops and the anode current appears). Since the thyristor opens, remove the gate voltage and make sure the anode current continues to flow.
- Then, decrease the thyristor voltage accurately and at every step measure the thyristor voltage and current, fill the measured values in the protocol, and plot the graph. Fix the hold point, i.e. the last non-zero point of this graph
- Following the instructor’s permission, switch off the devices, take off the circuit, and introduce proper order in the workplace.
Report contents
- Wiring diagram of the experimental setup with specification of the components.
- Circuit diagram of the experimental setup.
- Calculation of volltage dividers.
- Tables of the observed data UGC, IG and UF, IF.
- Scaled diagrams of the experimental input and output characteristics.
- Estimation of the hold voltage and hold current as well as the forward voltage drop ΔUF in the upper point of the output diagram.
- Conclusions regarding estimation, comparison and explanation of the expected and obtained results.
- Signed protocol.
Optional section
- Find experimentally the gate currents to open the thyristor at a couple of other UF voltages and build the firing diagram IG(UF).
- Using a signal generator and an oscilloscope, develop and employ the circuit to trace a voltage waveform UF(t) in the given point of the output diagram.
- Assemble the circuit and plot the forward and reverse output characteristics of the closed thyristor without the gate control.
- Calculate the thyristor input and output impedances, prove your calculation with simulation, and explain their differences.
- Calculate the thyristor input and output voltage drops at the highest current and prove your result with simulation.
- Calculate the thyristor input and output power dissipations at the highest current and prove your result with simulation.
Safety Diode Thyristor Transistor Opamp Triac

